Businesses rely on data to make crucial decisions every day, but the quality of their data analyses varies tremendously. Unless they have an in-house data science team, few companies have the bandwidth or expertise to sort through millions of data points in multiple formats and from various sources to uncover all the value locked within. Data discovery helps companies turn all of this data into useful insight without requiring deep IT knowledge.
Data discovery is a process of exploring data through visual tools that can help non-technical business leaders find new patterns and outliers to help an organisation better understand the insights their data has to offer. As a result, employees in every department can make smart business decisions and, just as importantly, continuously refine their approach. Whether seeking new efficiencies in warehouse processes or better ways to personalise social media activity, data discovery helps organisations uncover the nuggets of wisdom that turn their business intelligence into a dynamic and differentiating business asset.
What Is Data Discovery?
Data discovery is the process of navigating or applying advanced analytics to data to detect informative patterns that could not have been discovered otherwise. Like a golfer stepping back from the ball to assess the terrain before a putt, data discovery lets businesses take a step back from individual data points, combine data from multiple sources — including external third-party data — and see the big picture, which in turn leads to better decision-making and business strategy. So, when performing data discovery, you may not always know exactly what you’re looking for — you may simply be seeking patterns and outliers to better understand your data.
Crucially, data discovery does not require business users to build elaborate models. Most companies that use data discovery do so as part of their business intelligence (BI) software, which provides them with a complete view of their organisations in a simple dashboard or visual format.
Key Takeaways
- Data discovery is an iterative process that helps businesses extract valuable insight from multiple data streams so company leaders can make better decisions.
- Data discovery democratises data insight, allowing business users in every department to understand their customers and operations without IT or data expertise.
- Because the data discovery process often begins with cleaning up and preparing data for analysis, it’s useful in preventing dirty data from distorting ongoing business analyses.
- With the advent of artificial intelligence and machine learning, data discovery has advanced in recent years, enabling businesses to conduct increasingly complex analyses at scale.
Data Discovery Explained
Many organisations struggle with a breakdown in communication between data experts, business leaders and their teams who rely on data analyses to do their jobs. By extracting valuable insights from data so they can be easily shared and understood by all, data discovery is key to bridging this gap, as well as helpful in breaking down information silos within organisations.
Data discovery uses diagrams, text and visual storytelling to explain trends and convey other types of information. This means non-IT staff can understand large volumes of complex data and quickly extract the insight they need. In this way, data discovery democratises data analysis for every employee.
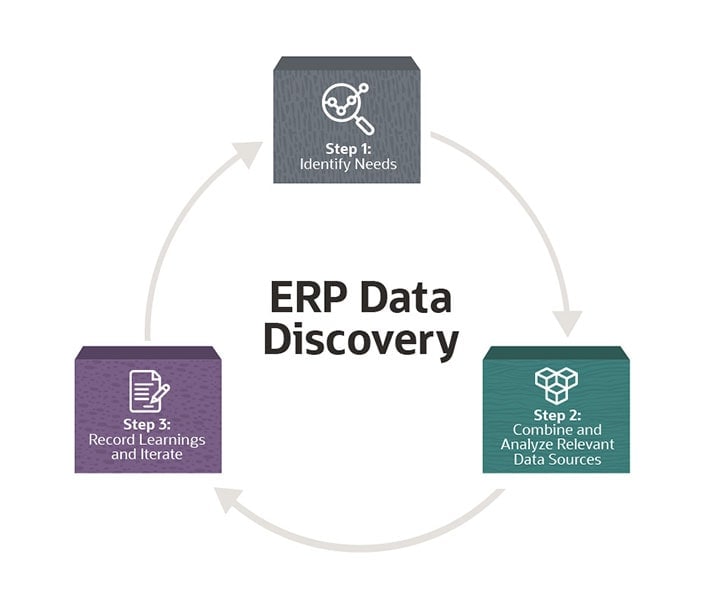
How Is Data Discovered?
Data discovery is a five-step process. It is also an iterative process, which means companies can continue to collect, analyse and refine their data discovery approach over time by drawing on their results and feedback from business stakeholders.
-
Step 1: Identify needs. Effective data discovery begins with a clear purpose, such as the resolution of a pain point. This means considering what kinds of data would be helpful to know, while remaining open to the unexpected insight along the way. For instance, a distributor of fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG) might decide to re-examine its logistics data in an effort to reduce food waste during shipment by 10%. Or a retail bank might analyse its web data with the aim of reducing bounce rates for new prospects.
-
Step 2: Combine data from relevant sources. For data discovery to be effective, it is important to combine and integrate data from multiple sources because no single data stream tells the complete story. This process is sometimes referred to as data crunching.
-
Step 3: Cleanse and prep the data. This is the heavy lifting part of data discovery — and a key part of its value. Cleaning the data and preparing it for analysis helps organisations reduce the “noise” in their data and get clearer direction from their data analyses.
-
Step 4: Analyse the data. With information combined from multiple departments, integrated with external data and cleansed for analysis, business leaders can gain a complete view of their operations and solve the operational riddles that stand in the way of efficiency.
-
Step 5: Record learnings and iterate. Data discovery is not a one-off process; it is a commitment to continuous improvement. In the bestseller book Outliers, author Malcolm Gladwell said it takes people 10,000 hours of practice to master a particular skill — and the same is true of businesses learning to master their data. They must treat data discovery as a way of life with the aim of improving and running more efficiently over time.
Why Is Data Discovery Important?
Agility is the hallmark of a successful business, and data discovery is part of the foundation of business agility. From the CIO charged with shifting teams to cloud-based solutions to the financial controller seeking new efficiencies in business reporting processes, data discovery gives business leaders and their teams an under-the-hood view of their operations so they can better understand and address any challenges at hand.
Indeed, data discovery continues to grow in popularity as more companies treat their data like an asset. The information businesses collect about their customers and operations has the potential to differentiate them from competitors. Data discovery allows them to turn this intelligence into a competitive advantage, whether in the form of product innovation, better customer experiences or efficiency gains.
History of Data Discovery
The history of data discovery reads like the history of the gold rush. The statisticians and economic analysts of the 1960s first referred to the process as data fishing, a negative term that referred to the blind nature of early data mining conducted without a predetermined hypothesis.
The process gained traction in the 1990s when the database community began to rely on data mining and a more open-ended form of data analysis to improve operations. With the establishment of the First International Conference on Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery (KDD-95) in Montreal in 1995, data discovery became a major focus for academic research.
The explosion of big data came next, followed by the data-driven decision-making and machine learning algorithms of recent years. As a result, data discovery has gone from an academic exercise to a must-have business process. Retailers, financial institutions, construction management firms and virtually every other industry uses data discovery to fuel smarter decision-making.
3 Categories of Data Discovery
Data discovery comes in multiple forms, combining analyses, modelling and visual outputs. To gain the most value from the process, businesses need to understand the interplay among their various data streams. With the help of visual discovery tools and business intelligence (BI) software, the following three categories of data discovery can help a company gain a big-picture view of its data in a single, easy-to-digest format.
Data Preparation
Data preparation is a crucial step that should come before any meaningful data discovery and analysis. It involves the cleaning, reformatting and merging of data from all sources so it can be analysed in a consistent format. In the same way a hockey player skates faster on sharpened blades, data discovery becomes more effective when businesses properly prepare their data. This might include deduplication, deleting null values, detecting outliers and any other ways to ensure only high-quality data goes through to data analysis.
Visual Analysis
Visualising data is one of the most effective ways to fully comprehend the insight it contains. Whether in the form of a chart, data flow diagram or dashboard, data visualisation helps those not trained in data science to understand the relationships among their various data streams in a way that feels intuitive. For example, design teams can easily learn how customers are using their products and adapt their work accordingly. And finance teams can get a snapshot of cost versus revenue for every department in the business and pinpoint areas for improvement.
Guided Advanced Analytics
Guided advanced analytics combines both descriptions and visuals to paint a complete picture of a company’s data. Where typical analytics output focuses on narrow descriptions of the data itself, guided analytics allow businesses to see the wider implications of their data discovery efforts, including the relationship among data streams from different teams and processes. Guided advanced analytics is particularly valuable for businesses navigating the shift to ecommerce, where the integration of web data with existing data streams is crucial to strategic decision-making.
Benefits of Data Discovery
Data discovery is a subset of business intelligence. It refers to the process of collecting and consolidating data from multiple databases into a single source, where it becomes easier to investigate and detect patterns. Below are five benefits of data discovery for businesses today.
-
A complete picture of company data: Data discovery provides businesses with a big-picture view of the many data streams in their organisations, allowing them to combine these streams in their analyses and develop well-rounded solutions to their challenges or customer needs. For instance, a retail bank can combine customer data from its website, mobile app, social platforms and ATMs to gain a more accurate view of each person it serves and better understand their behaviour.
-
Democratised insight and decision-making: IT and data expertise should not be a prerequisite to gain business insight. Data discovery makes data analysis understandable for stakeholders across the business, regardless of their data literacy. For instance, sales teams can see how their strategies drive or stop leads throughout the sales funnel, finance teams can spot and trim excess fat from their organisations’ operating expenses and marketers can tie together data from various customer touchpoints to see how their activities align with sales success. In short, data discovery has nearly limitless applications to match different business teams’ needs.
-
Improved risk management and compliance: As data volumes grow and governments become more invested in data protection, risk management and compliance have moved to the top of corporate agendas. Data discovery helps businesses spot outliers and potential threats in their data so they can manage them more proactively. Similarly, companies can stress-test their data management practices to ensure they comply with regulations like the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) and General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR).
-
Automatic data classification based on context: Companies collect more data from more sources and in new formats each day. Data discovery makes it possible to classify all of this information accurately based on the channel, conditions and context in which it is collected. For example, retailers can differentiate between customer data collected by their marketing, sales and service teams to assess their entire customer experience, rather than at a single moment in time.
-
Real-time data controls: Using predefined controls or contextual factors, companies can apply specific actions to the data they collect in real time, ensuring it is stored and analysed properly, and that data practices are secure and compliant. Data discovery is fundamental to developing this level of control.
Data Governance in Data Discovery
Data governance and data discovery go together hand-in-glove. Because data governance produces the policies and processes meant to guarantee quality in a business’s data, it contributes to the first category of data discovery: data preparation. Robust data governance can simplify and reduce the data preparation phase because it ensures that most data is already aligned with companywide definitions and formats.
In addition, a key tenet of most data governance strategies is centralisation of data storage, often in a data warehouse, which helps organisations maintain data security and compliance. Centralisation is also a prerequisite to effective data discovery. Centrally located data can be more readily accessed, shared and modified, ensuring that every team works with the latest information.
Processes for Data Discovery
Businesses collect enormous volumes of data about their customers and suppliers, in addition to data about their own operations. Moreover, they need to combine data streams from a mix of online and traditional systems from different channels such as mobile phones and tablets and from platforms like Facebook and other social networks.
Data discovery processes allow organisations to connect data from all of these sources, prepare it for analysis, share it among their internal teams and support crucial decision-making with valuable data-driven insight. Today, the emergence of artificial intelligence (AI) has added a new layer of sophistication to data discovery.
Whether using manual or advanced data discovery techniques, the process generally includes five steps — with continuous iteration.
- Understand what data is needed for the business analysis in question.
- Researchers must locate data sources that will provide that data.
- With all the necessary data located, set up a search query.
- Based on initial results, your data team will more deeply scrutinise the relevance of the data sources, eliminating irrelevant data and refining search queries accordingly.
- Researchers can evaluate the quality of their results and continue to reiterate these steps until they’re confident they have sound answers.
Manual vs. Smart Data Discovery
As with all data processes, the data discovery process just described was initially conducted by human brain power, also known as manual data discovery. Data experts had the task of consolidating and applying critical thinking to company data, after which they had to map out the flow of information across the organisation. These experts often set standards for data mining and discovery to bring consistency and clarity to their businesses’ approach.
Data discovery has evolved considerably in recent years thanks to technological advances, big data analysis and the emergence of powerful AI algorithms. Together, these tools have automated many data-related processes, including collection, preparation and visualisation. Smart data discovery — defined by global research and advisory firm Gartner as “a next-generation data discovery capability that provides business users or citizen data scientists with insights from advanced analytics” — is the latest step forward in this regard.
Companies that deploy smart data discovery use AI and machine learning to analyse large data volumes to uncover patterns that would be nearly impossible to detect manually. Not only are AI algorithms more effective at uncovering insights from multiple data sources, they also suggest ways to improve the data discovery process itself, be it through novel approaches to data preparation or the combination of data streams in new and unexpected ways.
Security in Data Discovery
To manage the growing volume and complexity of data they collect, businesses need sophisticated security measures to keep and protect their information, no matter the source or how it is being used. Data discovery is a priority for IT security teams, both to protect their data and to achieve data compliance.
Smart data discovery is ideally suited to this end, helping businesses spot anomalies, for example, in who is accessing certain data, and defend both themselves and customers against risk. AI algorithms allow for automated data monitoring and the enforcement of specific data protection policies. As a result, companies can better track, control and protect against threats, be they external ransomware attacks or employee error.
Specifically, data discovery helps businesses better find and classify data from different sources, spot and flag outliers and address issues before they turn into threats. With millions of dollars in fines issued in recent years to businesses around the world for inadequate data security measures, the imperative to shore up defences is not only operational, it’s a matter of financial viability and reputation in today’s data-driven economy.
Data Discovery Use Cases & Sample Problems
Data discovery has many applications, from improving back-end business operations to finding and removing complexity from the customer experience. With AI and machine learning algorithms allowing for more complex and ambitious data discovery exercises, the use cases will only continue to grow as businesses uncover new possibilities from their analyses. The following are just a few illustrative examples of how data discovery is making an impact.
-
Business planning: Data discovery can enhance many aspects of business planning. Consider the CFO who must make budget allocation decisions for the coming year based on departmental performance in the previous 12 months. Or perhaps it’s the IT leader who must assess the ROI of a new cloud implementation to inform the next phase of its rollout and eliminate inefficiencies.
-
Prospecting: Prospecting for new clients begins with an understanding of potential targets, their needs and their interests. However, incomplete data on prospects can lead to irrelevant targeting and turn off potential customers. Data discovery helps businesses collect and consolidate relevant data about each prospect into an accurate profile, which they can use to target customers in relevant and personalised ways.
-
Fraud prevention: Fraud is a major issue for businesses, particularly those operating online that face countless IT security threats each day. Data discovery is ideally suited to spot outliers in data so that companies can proactively address suspicious activity before it manifests as a hack or fraud. This goes for both external threats, like phishing emails, and internal issues linked to employee error.
-
Insurance claims: Insurance claims processing is a long and costly process prone to risk when done manually. Moreover, the longer it takes an insurance company to process a claim, the more likely it is to face legal issues with a claimant, which only adds to its costs. Data discovery speeds up the collection and processing of insurance claim data, while AI algorithms help companies spot potential fraud by comparing suspicious claims with historical data.
-
Social media analysis: Social media analysis is notoriously complex, forcing companies to adopt a range of platforms to manage customer relationships on these platforms. Data discovery helps them address customer issues more quickly, spotting complaints or behavioural trends in real time so they can be tackled before becoming bigger issues.
Tools for Data Discovery
There are a growing number of tools for data discovery, which are typically part of a business intelligence solution and cover at least one of the three main data discovery categories: data preparation, visual analysis and guided advanced analytics. With virtually limitless applications across most industries, these tools pave the way for all levels of employees, many of whom lack the expertise to access complex data sets from multiple sources and get the information they need on their own.
Advanced data discovery solutions, which are easily accessible when based in the cloud, allow for easy data navigation and search functionality. They should be capable of organising and preparing data, including easy-to-interpret visualisations, for analyses that can be shared throughout the organisation.
Future of Data Discovery
Where business intelligence helps with reporting and performance monitoring, data discovery promises to take BI analyses to the next level by helping business leaders and their teams in every department find and turn data into actionable insight. In addition to informing better decision-making, data discovery empowers leaders to scrutinise their processes and business models at a granular level and make improvements that add up to significant returns for their organisations.
Demand for data discovery tools will continue to rise as companies look to modernise their business intelligence and build their data analysis capabilities. An analysis by market research firm Research and Markets estimates that the global data discovery industry will be worth more than $14 billion by 2025. Every employee will need access to relevant data and insights to perform in their role, and data discovery will be the key to democratising insight. Algorithms will grow more powerful, visualisations will become more creative and companies in every industry will make data discovery a central part of their business planning and operations.
Organisations everywhere are digitising more elements of their operations as their customers embrace digital platforms to research, engage with and buy the products and services they need. In this increasingly data-rich business environment, data discovery serves as a bridge between companies’ priorities and their customers’ needs, making organisations more mindful of how they operate while ensuring customer data is put to good use — resulting in a better overall experience for all.
#1 Cloud ERP
Software
Data Discovery FAQs
What is data discovery?
Data discovery is the process of navigating or applying advanced analytics to data to detect informative patterns that would not have been discovered otherwise. Crucially, data discovery does not require business leaders and their teams to build elaborate models. Most companies use data discovery as part of their business intelligence (BI) software, which provides them with a complete view of their organisations in a simple dashboard or visual format.
What is the purpose of data discovery?
Data discovery provides businesses with a complete view of their organisations, giving stakeholders additional insight and context to inform business strategies and make smarter, more informed decisions.
What is data discovery in big data?
Data discovery is ideally suited to big data because it allows for rapid data analysis at scale. This is especially true of smart data discovery, which uses artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms to tackle complex analyses.
What is data discovery and classification?
Data discovery allows businesses to automatically classify data points based on predetermined rules and context. As a result, companies can better organise and track the growing volume of information they collect.
 Andy Morris
Andy Morris 







